What Are the Different Colors of the Northern Lights and What Do They Mean?
The Northern Lights, also known as aurora borealis, are a natural light display in the sky, primarily visible in high-latitude regions. These celestial wonders have captivated humans for centuries, inspiring awe, wonder, and cultural significance.
I. Causes Of The Northern Lights
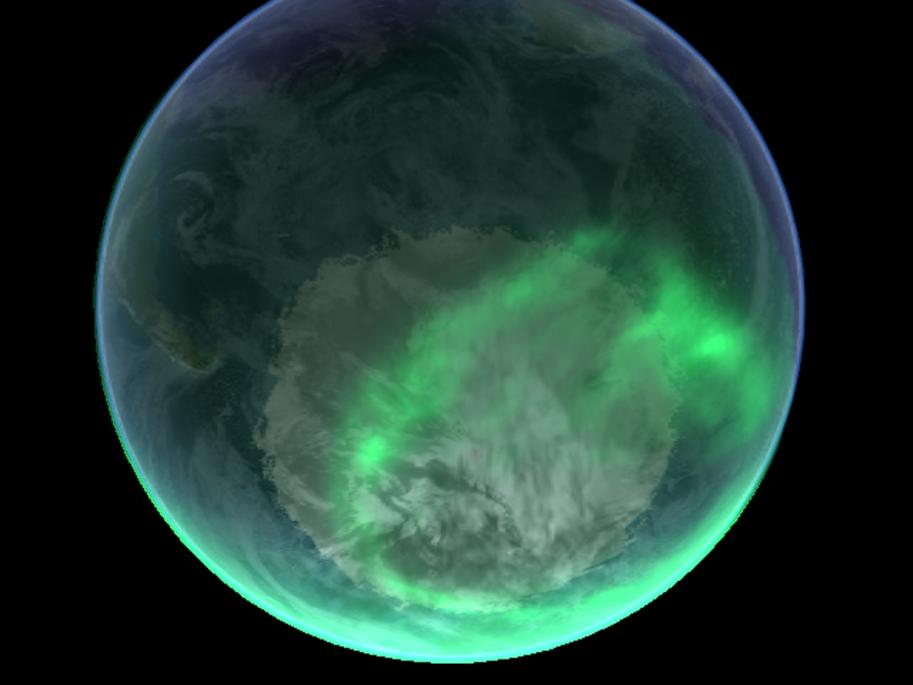
The Northern Lights are caused by the interaction between the solar wind and Earth's magnetic field. The solar wind, a stream of charged particles from the sun, interacts with Earth's magnetic field, causing the particles to spiral towards the poles. As these particles collide with atoms and molecules in the atmosphere, they excite them, causing them to emit light.
The color of the Northern Lights depends on the type of atom or molecule that is excited. Oxygen atoms, for example, produce green and red lights, while nitrogen atoms produce blue and purple lights. The altitude at which the particles collide also affects the color, with higher altitudes producing greener lights and lower altitudes producing redder lights.
II. Colors Of The Northern Lights
- Green: The most common color of the Northern Lights, caused by oxygen atoms at high altitudes. Wavelengths between 557.7 and 557.9 nanometers.
- Red: Less common, but more intense, caused by nitrogen atoms at higher altitudes. Wavelengths around 630 nanometers.
- Blue and Purple: Rare, but visually stunning, caused by helium and hydrogen atoms. Wavelengths below 500 nanometers.
- Yellow and Orange: Uncommon, but occasionally observed, caused by sodium and potassium atoms. Wavelengths between 589 and 630 nanometers.
III. Meaning And Symbolism Of The Colors
Different colors of the Northern Lights have been associated with cultural interpretations and beliefs. In some cultures, green lights are seen as a sign of good luck or prosperity, while red lights are associated with war or danger. Blue and purple lights are often seen as mystical or magical, while yellow and orange lights are associated with joy and celebration.
IV. Factors Influencing Color Variations
- Altitude of the aurora: Higher altitudes produce greener lights, while lower altitudes produce redder lights.
- Solar activity and geomagnetic storms: Increased solar activity and geomagnetic storms can lead to more intense and colorful auroras.
- Atmospheric conditions and cloud cover: Clear skies and dry air allow for better visibility of the Northern Lights.
V. Scientific Significance
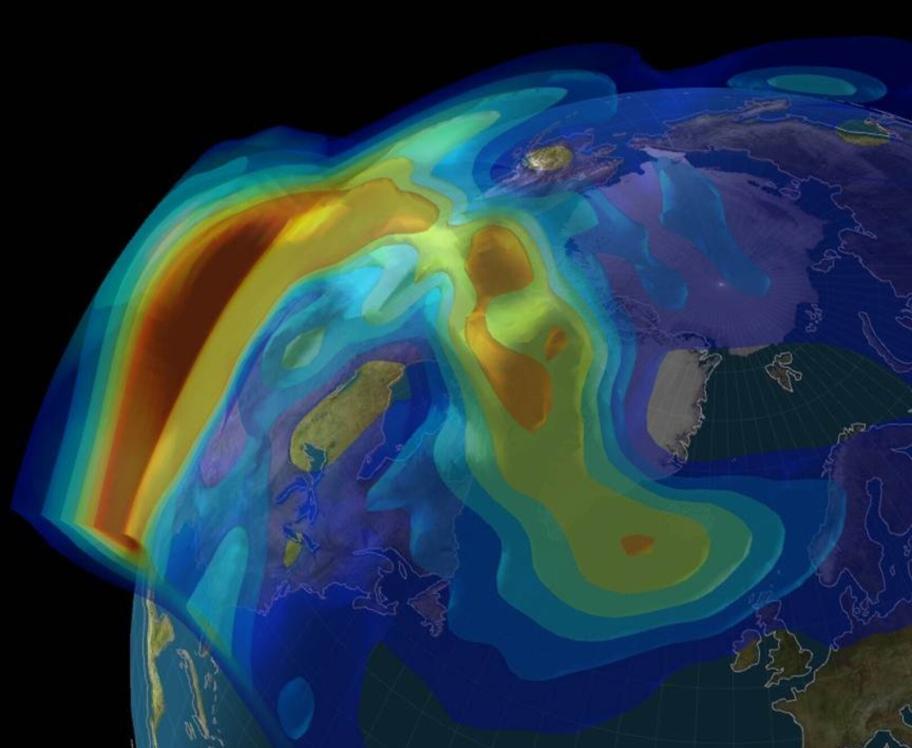
The Northern Lights play a crucial role in studying Earth's magnetosphere, the region of space around Earth influenced by its magnetic field. By observing the aurora, scientists can gain insights into the dynamics of the magnetosphere and its response to solar activity. Additionally, the Northern Lights can impact satellite communications and power grids, causing disruptions and power outages.
VI. Conclusion
The Northern Lights are a captivating natural phenomenon that has inspired awe and wonder for centuries. The different colors of the aurora, from vibrant greens to deep reds and rare blues and purples, add to their allure. Understanding the causes, colors, and cultural significance of the Northern Lights enhances our appreciation for this celestial spectacle and its scientific importance.
YesNo

Leave a Reply