How Do the Northern Lights Work?
The Northern Lights, also known as Aurora Borealis, are a natural phenomenon that has captivated humans for centuries. These mesmerizing displays of light in the sky are not only visually stunning but also scientifically fascinating. Let's delve into the science behind the Northern Lights and explore how they work.
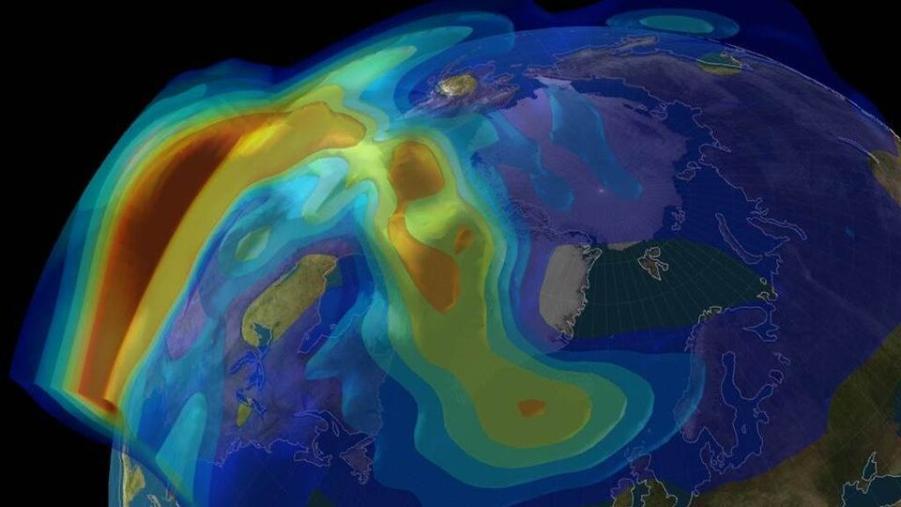
I. Scientific Explanation Of The Northern Lights
The Northern Lights are a result of the interaction between the Earth's magnetic field, solar wind, and the Earth's atmosphere. Here's a step-by-step explanation of the process:
- Earth's Magnetic Field: The Earth has a magnetic field that extends from its core to the outer space. This magnetic field is strongest at the poles and weakest at the equator.
- Solar Wind and Charged Particles: The Sun constantly emits a stream of charged particles known as solar wind. These particles travel through space and interact with the Earth's magnetic field.
- Interaction with Earth's Atmosphere: When the solar wind particles reach the Earth's magnetic field, they are guided towards the poles. As they approach the poles, they collide with atoms and molecules in the Earth's atmosphere.
- Collision and Excitation of Gas Molecules: The collision between the solar wind particles and the atmospheric gases causes the gas molecules to become excited. This means that the electrons in the gas molecules move to higher energy levels.
- Release of Energy as Light: As the excited gas molecules return to their normal energy levels, they release energy in the form of light. This light emission is what we see as the Northern Lights.
II. Colors And Patterns Of The Northern Lights
The Northern Lights display a variety of colors, including green, red, purple, and blue. The most common color is green, which is caused by the excitation of oxygen molecules in the atmosphere. Red auroras are less common and are caused by the excitation of nitrogen molecules. Purple and blue auroras are even rarer and occur under specific atmospheric conditions.
- Variations in Color Intensity and Distribution: The intensity and distribution of the Northern Lights can vary greatly. Some auroras are faint and barely visible, while others are so bright that they can be seen from hundreds of miles away. The auroral displays can also be localized or spread across the entire sky.
- Dynamic and Ever-Changing Displays: The Northern Lights are constantly changing and evolving. They can appear as curtains, rays, spirals, or even as a diffuse glow. The dynamic nature of the auroras is due to the continuous interaction between the solar wind and the Earth's magnetic field.
- Influence of Solar Activity and Geomagnetic Storms: The intensity and frequency of the Northern Lights are influenced by solar activity and geomagnetic storms. During periods of high solar activity, the solar wind is stronger and more intense, resulting in brighter and more frequent auroral displays. Geomagnetic storms can also trigger auroras at lower latitudes.
III. Location And Visibility Of The Northern Lights
The Northern Lights are primarily visible in high-latitude regions, such as Canada, Alaska, and Scandinavia. This is because the Earth's magnetic field lines are strongest at the poles, and the auroras occur along these lines. The best viewing conditions for the Northern Lights are dark, clear nights, away from city lights.
- High-Latitude Regions: The Northern Lights are most commonly seen in high-latitude regions, such as Canada, Alaska, Scandinavia, Iceland, and northern parts of Russia. These regions are located within the auroral zones, where the Earth's magnetic field lines converge.
- Best Viewing Conditions: The best viewing conditions for the Northern Lights are dark, clear nights, away from city lights. Light pollution can make it difficult to see the faint auroral displays.
- Seasonal and Time Variations in Visibility: The Northern Lights are most visible during the winter months, when the nights are longer. They are also more likely to occur during periods of high solar activity, which typically occur every 11 years.
- Aurora Ovals and Auroral Zones: The Northern Lights typically appear in a band or oval around the magnetic poles, known as the auroral oval. Within the auroral oval, there are regions of higher auroral activity called auroral zones.
IV. Impact Of The Northern Lights On Human Activity
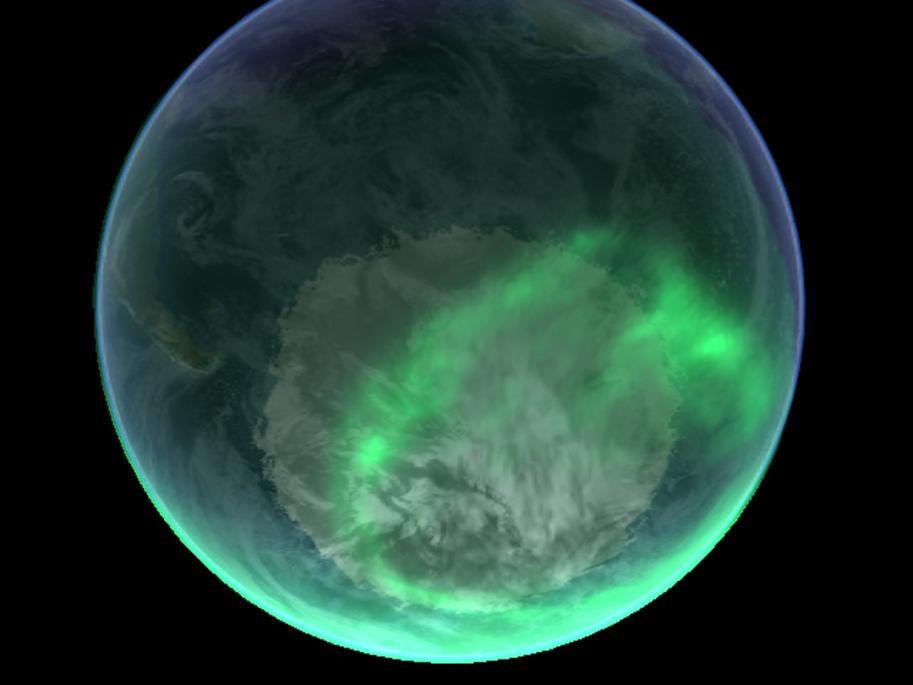
The Northern Lights have had a significant impact on human activity throughout history. Here are some notable effects:
- Cultural and Artistic Inspiration: The Northern Lights have been a source of inspiration for artists, writers, and musicians for centuries. They have been depicted in paintings, literature, and music, capturing the awe and wonder of the natural phenomenon.
- Tourism and Economic Benefits: The Northern Lights are a major tourist attraction, drawing visitors from around the world. This has led to economic benefits for regions where the auroras are visible, such as Alaska, Canada, and Scandinavia.
- Scientific Research and Space Weather Studies: The Northern Lights provide valuable insights into the Earth's magnetic field, solar wind, and the interactions between the Sun and the Earth. Scientists study the auroras to better understand space weather and its impact on Earth's systems.
- Potential Effects on Communication and Power Systems: The Northern Lights can sometimes interfere with communication and power systems. During periods of intense geomagnetic storms, the auroras can disrupt radio communications and cause power outages.
V. Summary Of Key Points
- The Northern Lights are caused by the interaction between the Earth's magnetic field, solar wind, and the Earth's atmosphere.
- The auroras occur when charged particles from the solar wind collide with atoms and molecules in the atmosphere, causing them to emit light.
- The most common color of the Northern Lights is green, but they can also appear in red, purple, and blue.
- The Northern Lights are primarily visible in high-latitude regions, such as Canada, Alaska, and Scandinavia.
- The best viewing conditions for the Northern Lights are dark, clear nights, away from city lights.
- The Northern Lights have had a significant impact on human activity, including cultural inspiration, tourism, scientific research, and potential effects on communication and power systems.
Ongoing Research And Future Discoveries
Scientists continue to study the Northern Lights to better understand their behavior and the underlying processes that drive them. Ongoing research focuses on topics such as the relationship between solar activity and auroral displays, the impact of geomagnetic storms on the auroras, and the potential effects of climate change on the Northern Lights.
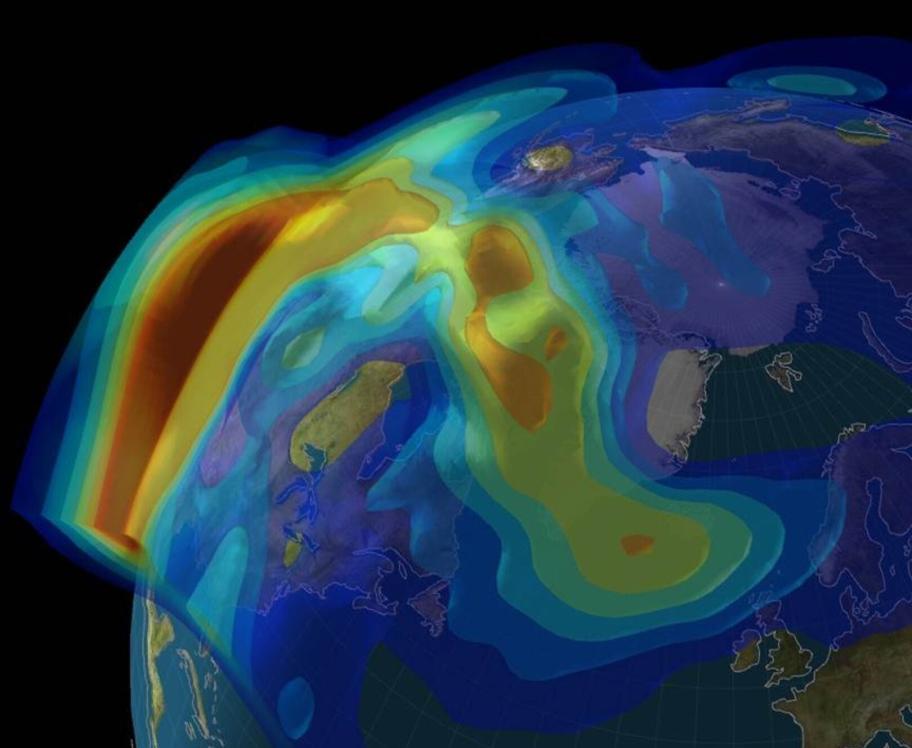
As our understanding of the Northern Lights continues to evolve, we can expect to uncover new insights into this captivating natural phenomenon and its significance in the Earth's system.
The Northern Lights are a testament to the beauty and complexity of the natural world. They remind us of our connection to the Sun and the vastness of the universe. Whether you've witnessed the Northern Lights firsthand or dream of seeing them one day, their allure and wonder continue to inspire and captivate people around the world.
YesNo

Leave a Reply