Unveiling the Enchantment: What Causes the Northern Lights and How Do They Work?
The Northern Lights, also known as Aurora Borealis, are a natural phenomenon that has captivated people for centuries. These mesmerizing displays of light occur in the high-latitude regions of both the northern and southern hemispheres, painting the night sky with vibrant colors and dancing patterns.
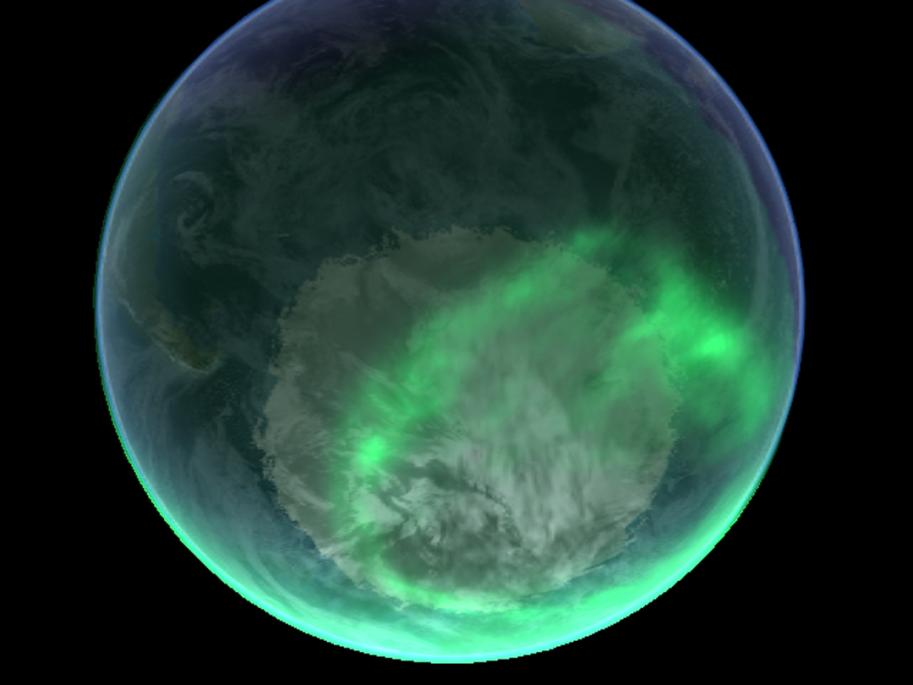
I. Scientific Explanation Of The Northern Lights
The Northern Lights are a result of the interaction between the Earth's magnetic field and charged particles from the sun known as solar wind. Here's a step-by-step explanation of the process:
- Solar Wind Particles: The sun constantly emits a stream of charged particles called solar wind. These particles travel through space and interact with the Earth's magnetic field.
- Magnetic Field Interaction: The Earth's magnetic field acts like a shield, deflecting most of the solar wind particles. However, some particles are able to penetrate the magnetic field and are guided towards the magnetic poles.
- Collision with Atmospheric Gases: As the solar wind particles approach the magnetic poles, they collide with atoms and molecules of the Earth's atmosphere, primarily oxygen and nitrogen.
- Excitation and Energy Release: The collisions between the solar wind particles and atmospheric gases cause the atoms and molecules to become excited. When these excited atoms and molecules return to their normal state, they release energy in the form of colorful light.
II. Colors And Patterns Of The Northern Lights
The Northern Lights can display a wide range of colors, each corresponding to a specific atmospheric gas:
- Green: The most common color of the Northern Lights, green is produced by the excitation of oxygen atoms.
- Red: Less common than green, red is caused by the excitation of nitrogen atoms.
- Purple and Blue: These colors are produced by a combination of excited oxygen and nitrogen atoms.
The Northern Lights can also take on various shapes and patterns, including curtains, rays, and coronas. These patterns are influenced by the direction and intensity of the solar wind, as well as the Earth's magnetic field lines.
III. Factors Influencing The Northern Lights
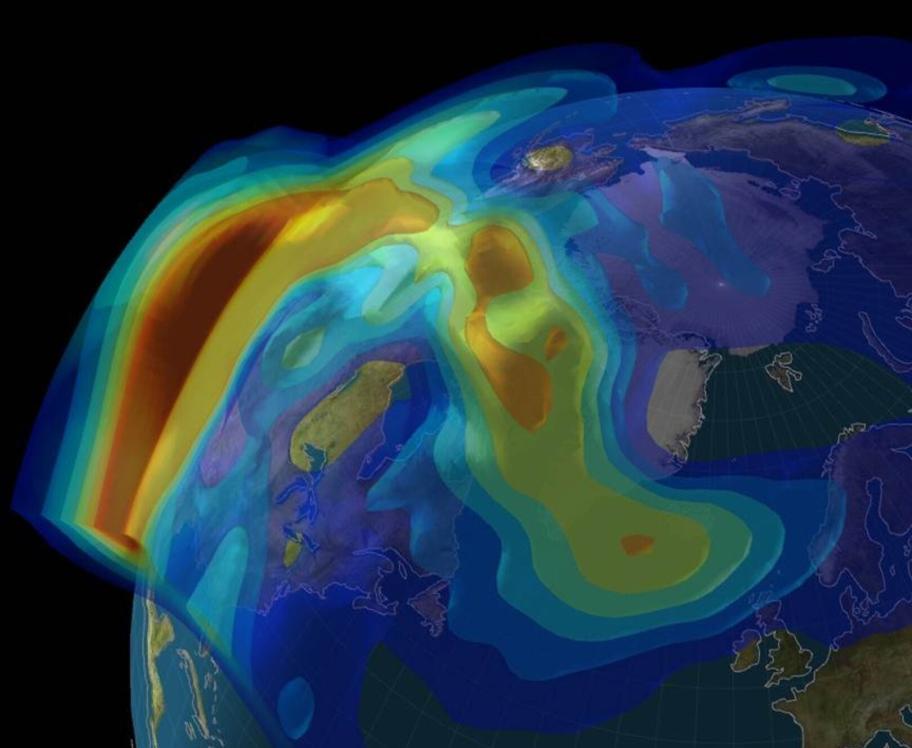
The intensity and frequency of the Northern Lights are influenced by several factors:
- Solar Activity: Solar storms and coronal mass ejections can enhance the Northern Lights by releasing large amounts of solar wind particles. During these periods, the Northern Lights may be more frequent and more vibrant.
- Geomagnetic Storms: Geomagnetic storms, caused by disturbances in the Earth's magnetic field, can also lead to more spectacular Northern Lights displays.
IV. Cultural Significance And Folklore
The Northern Lights have held cultural and historical significance in various cultures throughout history:
- Legends and Myths: Many cultures have legends and myths associated with the Northern Lights. In some cultures, they are seen as a sign of good luck or a connection to the spirit world.
- Artistic Representations: The Northern Lights have been a source of inspiration for artists, writers, and musicians throughout history. They have been depicted in paintings, literature, and music, capturing their beauty and mystery.
V. Conclusion
The Northern Lights are a captivating natural phenomenon that continues to inspire awe and wonder. Their beauty and complexity are a testament to the intricate workings of our planet and its interaction with the sun. Whether you're lucky enough to witness the Northern Lights in person or simply admire them through photographs and videos, these celestial displays are a reminder of the magic and mystery that still exist in our world.
YesNo

Leave a Reply