What Causes the Different Colors of the Northern Lights?
The Northern Lights, also known as Aurora Borealis, are a captivating natural phenomenon that has mesmerized people for centuries. These celestial displays of light occur in the high-latitude regions of both the northern and southern hemispheres. This article delves into the science behind the Northern Lights, explaining the causes of their diverse colors.
The Science Behind The Northern Lights
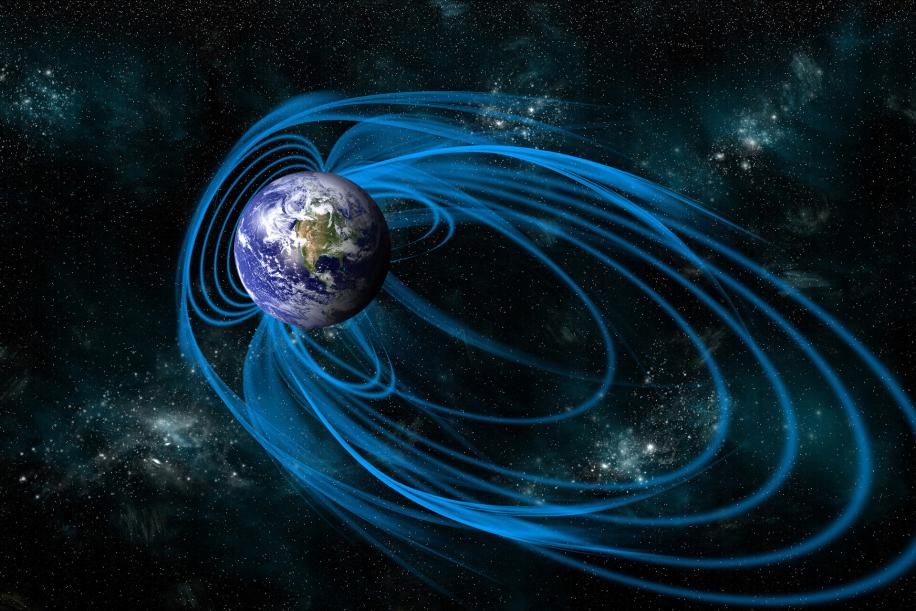
Solar Wind And Magnetosphere
The Northern Lights are a result of the interaction between the solar wind and Earth's magnetic field. The solar wind consists of charged particles, primarily protons and electrons, that are continuously emitted from the Sun. When these particles reach Earth, they encounter the planet's magnetic field, which guides them towards the magnetic poles.
As the charged particles approach the magnetic poles, they are funneled into the magnetosphere, a region of space surrounding Earth where the magnetic field is strongest. Within the magnetosphere, the charged particles spiral along the magnetic field lines, gaining energy as they move.
Charged Particles And Collisions
As the charged particles spiral within the magnetosphere, they collide with atoms and molecules of the Earth's atmosphere. These collisions excite the atoms and molecules, causing them to transition to higher energy levels. When the excited atoms and molecules return to their ground state, they release energy in the form of light, giving rise to the Northern Lights.
Energy Levels And Light Emission
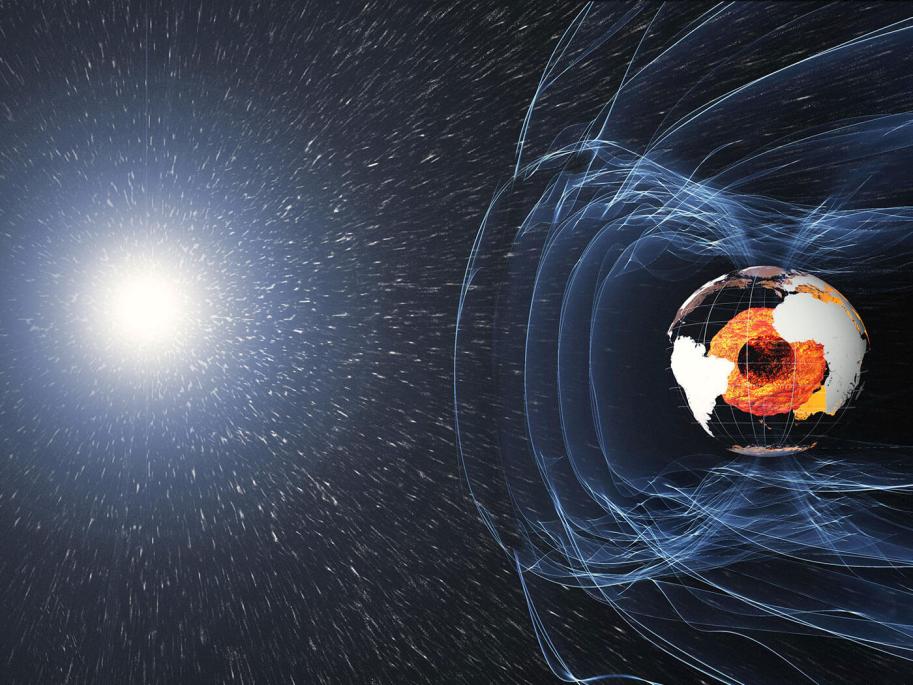
The color of the Northern Lights depends on the type of atom or molecule that is excited and the energy level to which it is excited. Different atoms and molecules have different energy levels, and when they return to their ground state, they emit light of specific wavelengths, corresponding to specific colors.
The Colors Of The Northern Lights
Green: The Most Common Color
Green is the most prevalent color of the Northern Lights. This is primarily due to the abundance of oxygen atoms in the Earth's atmosphere. When oxygen atoms are excited by the charged particles, they emit green light.
Red, Blue, And Purple: Less Common Colors
Red, blue, and purple are less common colors of the Northern Lights. These colors are produced when nitrogen and helium atoms are excited by the charged particles. Nitrogen atoms emit red and blue light, while helium atoms emit purple light.
Other Rare Colors: Yellow, Orange, And Pink
Yellow, orange, and pink are rare colors of the Northern Lights. These colors are produced when hydrogen atoms are excited by the charged particles. However, hydrogen atoms are relatively scarce in the Earth's atmosphere, making these colors less frequently observed.
Factors Influencing The Color Variations
Solar Activity And Geomagnetic Storms
The intensity and colors of the Northern Lights are influenced by solar activity. During periods of high solar activity, such as solar flares and coronal mass ejections, the solar wind is more intense and carries more charged particles. This results in brighter and more colorful displays of the Northern Lights.
Altitude And Atmospheric Composition
The colors of the Northern Lights also vary with altitude. At lower altitudes, the atmosphere is denser, and the charged particles collide with more atoms and molecules. This produces a greater variety of colors, including red, blue, and purple. At higher altitudes, the atmosphere is thinner, and the charged particles collide with fewer atoms and molecules. This results in a predominantly green aurora.
Geographic Location And Viewing Conditions
The visibility and colors of the Northern Lights are influenced by geographic location and viewing conditions. The Northern Lights are best visible in high-latitude regions, such as Alaska, Canada, Scandinavia, and Iceland. Clear skies and darkness are essential for optimal viewing conditions.
The Northern Lights are a mesmerizing natural phenomenon that showcases the dynamic and ever-changing nature of our planet and its interaction with the Sun. The colors of the Northern Lights are a result of the complex interplay between solar wind, Earth's magnetic field, atmospheric gases, and energy levels. Witnessing the Northern Lights firsthand is a truly awe-inspiring experience that leaves an unforgettable impression on the viewer.
YesNo

Leave a Reply