What are the Northern Lights and How Do They Form?
The Northern Lights, also known as Aurora Borealis, are a natural light display in the Earth's sky, primarily visible in high-latitude regions. These celestial phenomena have captivated humanity for centuries, inspiring awe and wonder.

I. Scientific Explanation
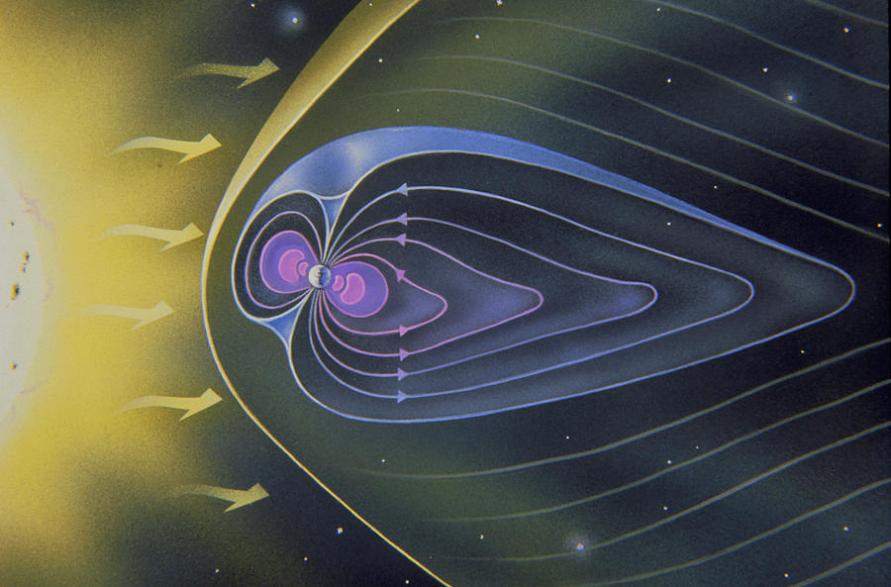
The Earth's Magnetic Field:
The Earth's magnetic field is a protective shield that extends from the planet's core to the outer space. It acts as a guide for charged particles from the sun, known as solar wind.
Solar Wind And Its Interaction:
The solar wind, composed of charged particles, constantly streams from the sun. When these particles encounter the Earth's magnetic field, they are guided towards the poles.
Formation Of The Auroral Oval:
As the charged particles approach the poles, they interact with the Earth's atmosphere. This interaction creates an oval-shaped region, known as the auroral oval, where the Northern Lights are most frequently observed.
Role Of Charged Particles And Collisions:
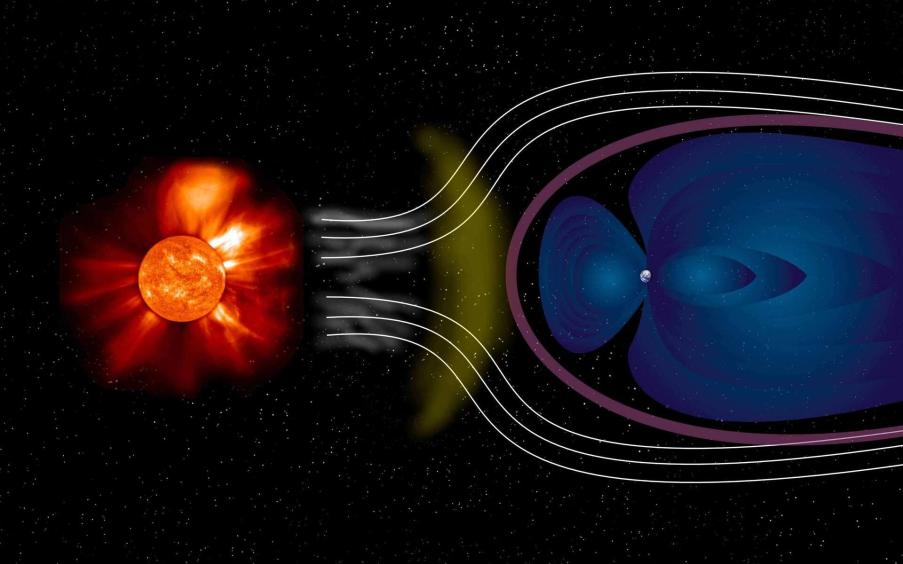
The charged particles from the solar wind collide with atoms and molecules in the atmosphere, causing them to become excited. When these excited particles return to their normal state, they release energy in the form of light, creating the vibrant colors of the aurora.
II. Colors And Patterns
Explanation Of Different Colors:
The colors of the Northern Lights vary depending on the type of atmospheric gases that the charged particles collide with. Nitrogen produces green and red hues, while oxygen emits blue and purple lights.
Factors Influencing Color Variations:
- Altitude: The higher the altitude, the more likely the particles will collide with oxygen, resulting in blue and purple colors.
- Solar Activity: During periods of high solar activity, the aurora can exhibit brighter and more intense colors.
Common Patterns And Shapes:
- Curtains: Long, flowing curtains of light that hang from the sky.
- Rays: Narrow beams of light that shoot up from the horizon.
- Arcs: Large, semicircular bands of light that stretch across the sky.
III. Geographical Occurrence
Regions Of Visibility:
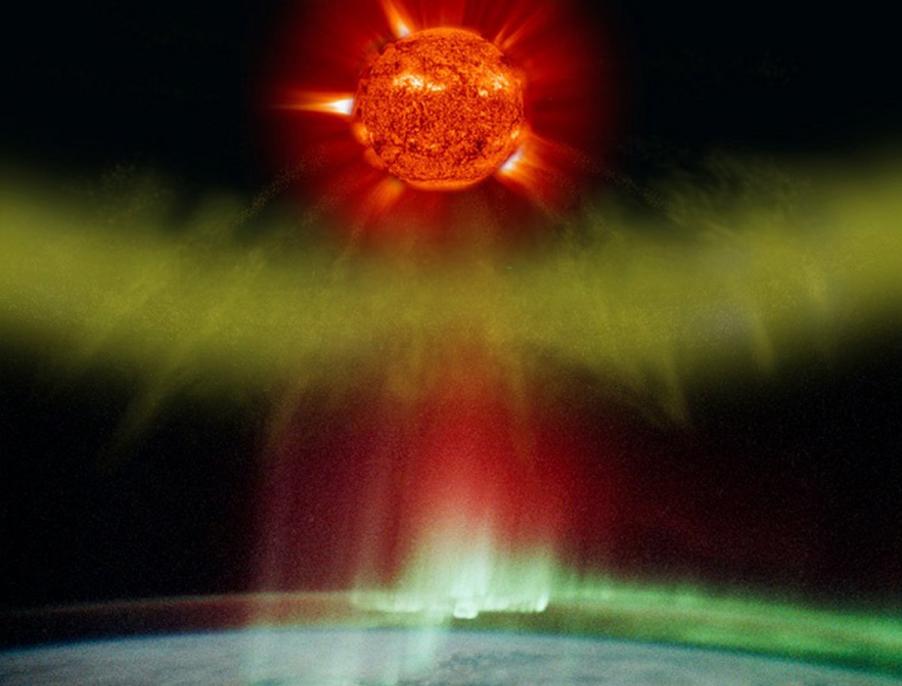

The Northern Lights are primarily visible in high-latitude regions, such as Alaska, Canada, Scandinavia, and Iceland. However, they can sometimes be seen in lower latitudes during periods of intense solar activity.
Best Viewing Locations And Times:
- Dark Skies: Areas with minimal light pollution offer the best viewing conditions.
- Winter Months: The aurora is most frequently observed during the winter months when the nights are longer.
- Clear Skies: Clear skies are essential for optimal viewing.
Seasonal And Solar Activity Factors:
The Northern Lights are more likely to occur during periods of high solar activity, such as the peak of the 11-year solar cycle. Additionally, the aurora is more prominent during the spring and fall seasons.
IV. Impact On Earth's Atmosphere
Effects On Ionosphere And Thermosphere:
The Northern Lights can affect the ionosphere and thermosphere, the upper layers of the Earth's atmosphere. These effects can disrupt radio communications and GPS signals.
Geomagnetic Storms And Consequences:
During intense solar activity, geomagnetic storms can occur. These storms can cause power outages, disrupt satellite communications, and even damage electrical grids.
Potential Impact On Satellite Communications And Power Grids:
The Northern Lights can have a significant impact on satellite communications and power grids, particularly in high-latitude regions. Geomagnetic storms can disrupt these systems, causing outages and potential damage.
V. Cultural And Historical Perspectives
Myths And Legends:
The Northern Lights have inspired numerous myths and legends throughout history. In many cultures, they were seen as a sign of good luck, a warning of impending events, or a connection to the spirit world.
Artistic Representations And Cultural Significance:
The Northern Lights have been depicted in art, literature, and music for centuries. They have been a source of inspiration for artists, writers, and musicians, capturing the awe and wonder of this natural phenomenon.
Role In Folklore And Storytelling:
The Northern Lights have played a significant role in folklore and storytelling, often associated with supernatural beings, magical events, and celestial omens.
VI. Scientific Research And Exploration
Ongoing Studies And Research Projects:
Scientists continue to study the Northern Lights to better understand their formation, behavior, and impact on the Earth's atmosphere. Research projects aim to unravel the mysteries of the aurora and its connection to solar activity.
Technological Advancements In Observation:
Technological advancements have enabled scientists to observe and study the Northern Lights in greater detail. Satellites, ground-based observatories, and specialized cameras have provided valuable insights into the dynamics and characteristics of the aurora.
Future Prospects For Exploration And Understanding:
The future holds exciting prospects for exploring and understanding the Northern Lights. Space missions and advanced observation techniques may provide new insights into the interactions between the solar wind and the Earth's magnetic field, leading to a deeper comprehension of this celestial spectacle.
VII. Conclusion
The Northern Lights are a captivating natural phenomenon that has fascinated humanity for centuries. Their scientific explanation lies in the interaction between the solar wind and the Earth's magnetic field, resulting in a mesmerizing display of colors and patterns. The aurora's impact on the Earth's atmosphere and its cultural and historical significance make it a subject of ongoing scientific research and exploration. As we continue to unravel the mysteries of the Northern Lights, we can appreciate their beauty and importance as a natural wonder.
YesNo

Leave a Reply