Future Exploration: What Unanswered Questions Remain About the Northern Lights?
In the vast expanse of the night sky, few celestial displays capture the imagination and awe of observers like the Northern Lights. These mesmerizing curtains of light, dancing across the heavens in vibrant hues, have captivated cultures and inspired legends for centuries. Yet, despite their enduring presence, many unanswered questions surround these enigmatic phenomena, beckoning scientists and enthusiasts alike to delve deeper into their mysteries.
Historical And Cultural Significance
The Northern Lights, also known as aurora borealis, have held a profound place in human history and culture. Across various regions and civilizations, these celestial displays have been revered, feared, and celebrated.
- In Norse mythology, the Northern Lights were believed to be the shimmering armor of the Valkyries, guiding fallen warriors to Valhalla.
- Inuit legends spoke of the aurora as the spirits of the dead dancing in the sky.
- Japanese folklore associated the Northern Lights with foxes, believed to be messengers between the spirit world and the living.
These celestial displays have not only inspired myths and legends but also influenced artistic expressions throughout history. From paintings and poetry to music and dance, the Northern Lights have served as a muse for countless creative minds.
Current Understanding Of The Northern Lights

While scientific understanding of the Northern Lights has advanced significantly, many aspects of these phenomena remain enigmatic.
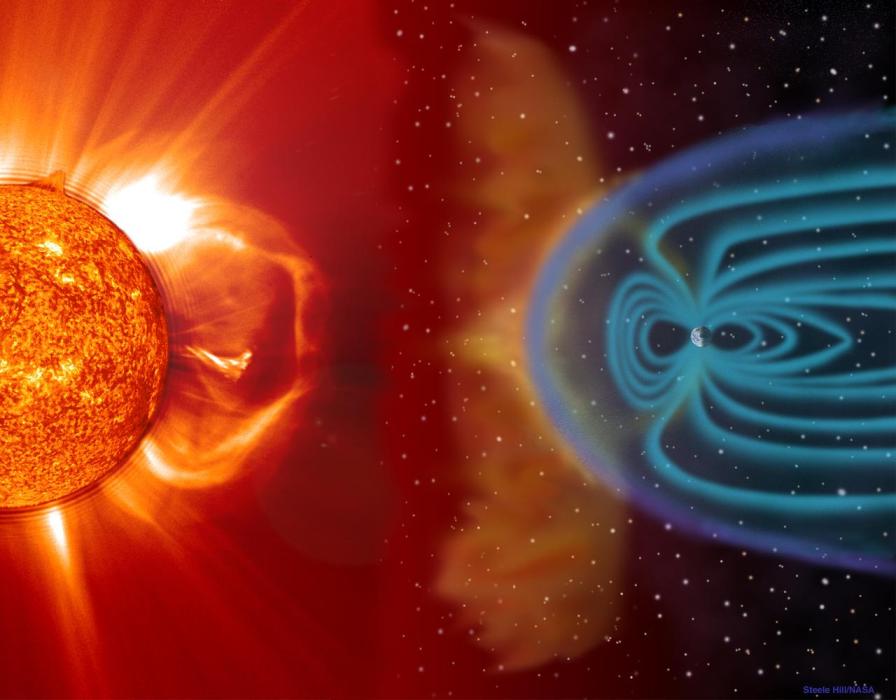
- Solar Activity and the Earth's Magnetic Field: The Northern Lights are primarily caused by the interaction between charged particles from the sun (solar wind) and the Earth's magnetic field. As these particles enter the Earth's atmosphere, they collide with atoms and molecules, causing them to emit light.
- Colors and Shapes: The colors of the Northern Lights vary depending on the type of atmospheric gas that the solar particles collide with. Oxygen typically produces green and red auroras, while nitrogen emits blue and purple hues. The shapes and patterns of the aurora are influenced by factors such as the strength of the solar wind and the configuration of the Earth's magnetic field.
- Regions of Visibility: The Northern Lights are primarily visible in high-latitude regions, such as Alaska, Canada, Scandinavia, and northern Russia. However, under exceptional circumstances, they can be observed at lower latitudes during periods of intense solar activity.
Unanswered Questions And Ongoing Research
Despite our current understanding, numerous unanswered questions continue to intrigue scientists and fuel ongoing research.
- Trigger Mechanisms: The exact mechanisms that trigger the formation of the Northern Lights are not fully understood. Scientists are investigating the role of solar wind speed, density, and magnetic field configuration in initiating and shaping auroral displays.
- Variations in Intensity and Frequency: The intensity and frequency of the Northern Lights vary significantly over time. Researchers aim to understand the factors that influence these variations, including the 11-year solar cycle and the role of geomagnetic storms.
- Impact of Climate Change: The potential impact of climate change on the Northern Lights is an emerging area of research. Some studies suggest that changes in atmospheric composition and temperature may affect the occurrence and characteristics of auroral displays.
- Predicting Auroras: Scientists are working on developing methods to predict the occurrence and characteristics of the Northern Lights. Accurate predictions would enable better planning for scientific observations, tourism, and space exploration activities.
Technological Advancements And New Discoveries
Recent technological advancements have opened new avenues for exploring and understanding the Northern Lights.
- Satellite Observations: Satellites equipped with specialized instruments provide valuable data on solar activity, the Earth's magnetic field, and auroral emissions. These observations help scientists monitor and study auroral displays in unprecedented detail.
- Ground-Based Observatories: Ground-based observatories equipped with cameras, spectrometers, and other instruments collect data on the Northern Lights from various locations. These observations complement satellite data and provide insights into local variations and dynamics of auroral displays.
- Computational Modeling and Simulations: Scientists use computer models to simulate the interactions between solar particles and the Earth's magnetic field. These simulations help researchers gain a better understanding of the processes that create the Northern Lights and predict their behavior.
- Citizen Science Initiatives: Citizen science projects engage the public in collecting data on the Northern Lights. These initiatives provide valuable observations that contribute to scientific research and raise awareness about these celestial phenomena.
Future Directions And Challenges
Future research on the Northern Lights faces both challenges and opportunities.
- Long-Term Data Collection: Long-term data collection and analysis are crucial for understanding the variability and trends in auroral activity. This requires sustained funding and international collaboration to maintain and expand observation networks.
- International Collaboration: International collaboration is essential for sharing data, resources, and expertise. Collaborative efforts can lead to more comprehensive and accurate understanding of the Northern Lights and their global impact.
- Role of Citizen Scientists: Citizen scientists can play a significant role in collecting data on the Northern Lights. Public engagement initiatives can help expand the scope of observations and raise awareness about these celestial displays.
- Ethical Considerations: Research on the Northern Lights should be conducted with ethical considerations in mind. This includes respecting Indigenous knowledge and cultural beliefs associated with these phenomena.
The Northern Lights, with their captivating beauty and enigmatic nature, continue to inspire awe and curiosity. As scientists delve deeper into the mysteries surrounding these celestial displays, they uncover new insights that contribute to our understanding of the Earth's magnetic field, solar activity, and the dynamic processes that shape our planet's environment. By embracing future exploration and addressing unanswered questions, we can unlock the secrets of the Northern Lights and gain a deeper appreciation for the wonders of our universe.
YesNo

Leave a Reply